- 品名: Brilliant Violet 421? anti-mouse CD4 Antibody
- 型號(hào): 100443
- 產(chǎn)品詳情
- 規(guī)格參數(shù)
Isotype Control
Verified Reactivity
Mouse
Antibody Type
Monoclonal
Host Species
Rat
Immunogen
Mouse CTL clone V4
Formulation
Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).
Preparation
The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Brilliant Violet 421? under optimal conditions.
Concentration
μg sizes: 0.2 mg/mL
μL sizes: lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration, please enter the lot number in our Concentration and Expiration Lookup or Certificate of Analysis online tools.)Storage & Handling
The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
Application
Recommended Usage
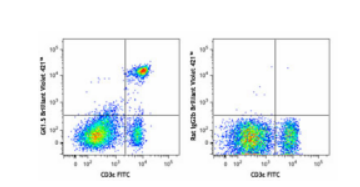
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining using the μg size, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.125 μg per million cells in 100 μl volume. For flow cytometric staining using the μl size, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 μl per million cells in 100 μl staining volume or 5 μl per 100 μl of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
Brilliant Violet 421? excites at 405 nm and emits at 421 nm. The standard bandpass filter 450/50 nm is recommended for detection. Brilliant Violet 421? is a trademark of Sirigen Group Ltd.
Learn more about Brilliant Violet?.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents.Excitation Laser
Violet Laser (405 nm)
Application Notes
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: blocking of CD4+ T cell activation1,4,11, thymocyte costimulation3, in vitro and in vivo depletion2,5-8, blocking of egg-sperm cell adhesion1,4, immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections9,10, immunoprecipitation1,2, and spatial biology (IBEX)12,13. The GK1.5 antibody is able to block CD4 mediated cell adhesion and T cell activation. Binding of GK1.5 antibody to CD4 T cells can be blocked by RM4-5 antibody, but not RM4-4 antibody. For in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF? purified antibody (Cat. No. 100442) with a lower endotoxin limit than standard LEAF? purified antibodies (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/μg).
Additional Product Notes
Iterative Bleaching Extended multi-pleXity (IBEX) is a fluorescent imaging technique capable of highly-multiplexed spatial analysis. The method relies on cyclical bleaching of panels of fluorescent antibodies in order to image and analyze many markers over multiple cycles of staining, imaging, and, bleaching. It is a community-developed open-access method developed by the Center for Advanced Tissue Imaging (CAT-I) in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID, NIH).
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation)Dialynas DP, et al. 1983. J. Immunol. 131:2445. (Block, IP)
Dialynas DP, et al. 1983. Immunol. Rev. 74:29. (IP, Deplete)
Wu L, et al. 1991. J. Exp. Med. 174:1617. (Costim)
Godfrey DI, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 152:4783. (Block)
Gavett SH, et al. 1994. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 10:587. (Deplete)
Schuyler M, et al. 1994. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 149:1286. (Deplete)
Ghobrial RR, et al. 1989. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 52:486. (Deplete)
Israelski DM, et al. 1989. J. Immunol. 142:954. (Deplete)
Zheng B, et al. 1996. J. Exp. Med. 184:1083. (IHC)
Frei K, et al. 1997. J. Exp. Med. 185:2177. (IHC)
Felix NJ, et al. 2007. Nat. Immunol. 8:388. (Block)
Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
Product Citations
Cignarella F et al. 2018. Cell metabolism. 27(6):1222-1235 . PubMed
Xu J et al. 2018. Cell. 173(3):762-775 . PubMed
Garg G et al. 2019. Cell reports. 26(7):1854-1868 . PubMed
Goswami M, et al. 2019. Biomed Opt Express. 10:151. PubMed
Yue X, et al. 2019. Nat Commun. 10:2011. PubMed
Bennion BG, et al. 2019. J Virol. 93. PubMed
Silva DA, et al. 2019. Nature. 565:186. PubMed
Maluski M, et al. 2019. J Clin Invest. 129:5108. PubMed
Runge EM, et al. 2020. J Neuroinflammation. 17:121. PubMed
Annu K, et al. 2020. Sci Rep. 10:2359. PubMed
Han Y, et al. 2020. Nat Commun. 11:1776. PubMed
Huai W, et al. 2019. J Exp Med. 216:772. PubMed
RRID
AB_10900241 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100437)
AB_2562557 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100443)
AB_11203718 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100438)



